In this post, we are going to do an Access export to Excel, and you’ll see the VBA we’ll work with.
This Excel automation will create a worksheet for each of our data points, and then enter the row items for that data point.
We are going to let Access do most of the querying and “heavy lifting”, because that’s what it’s pretty good at.
So rather than create a few small queries and trying to link them in Excel, we will do all the linking in one Access query and send that result over to Excel.
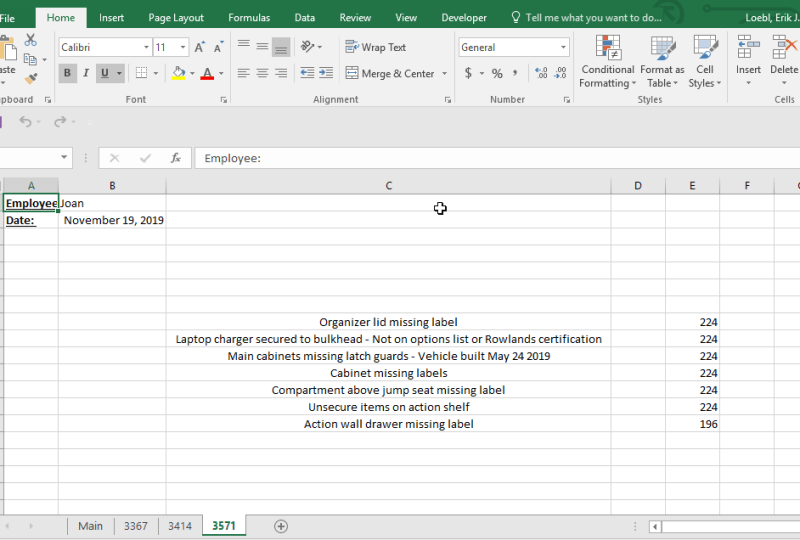
In this image you’ll see the data we will be exporting to Excel
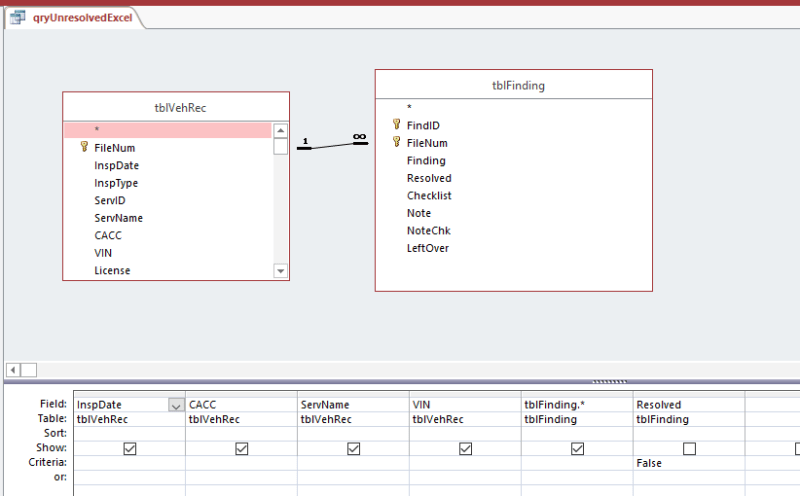
In this image you are going to find out that the data for the query is coming from multiple tables. So the idea is to join all the table data in Access, and then send it to Excel
The query here is going to be called “qryUnresolvedExcel”, and its sole purpose is to gather the data necessary for the Excel export.
In the beginning the Excel workbook will only have one worksheet “Main”:
The comments on the code will help decipher what going on:
Private Sub btnExcel_Click()
ExcelExport
MsgBox "Excel Export Complete"
End Sub
Private Sub ExcelExport()
Dim rst As Recordset
Dim rstUnique As Recordset
Dim strSQL As String
'Dim objExcelBook As Excel.Workbook
'Dim objExcelSheet As Excel.Worksheet
'USING EARLY BINDING
'Dim objExcelApp As Excel.Application
'Dim objExcelBook As Excel.Workbook
'Dim objExcelSheet As Excel.worksheet
''USING LATE BINDING
Dim objExcelApp As Object
Dim objExcelBook As Object
Dim objExcelSheet As Object
Dim strTemplate As String
Dim intExcelMainRow As Integer
Dim intExcelMainColumn As Integer
Dim intExcelDetailRow As Integer
Dim intExcelDetailColumn As Integer
Dim strWhere As String
Dim strSQLUnique As String
Dim intCaccRows As Integer
Dim strMainSheet As String
Dim strNewSheet As String
strTemplate = CurrentProject.Path & "\report.xlsx"
'Set m_objExcelApp = New Excel.Application
On Error Resume Next
DoCmd.Hourglass True
If Len(Me.Filter) = 0 Then
strSQLUnique = "SELECT DISTINCT CACC FROM qryUnresolvedExcel "
Else
strSQLUnique = "SELECT DISTINCT CACC FROM qryUnresolvedExcel WHERE " & Me.Filter
End If
'-------------------------------------------------------------
Set rstUnique = CurrentDb.OpenRecordset(strSQLUnique)
'this is a sheet in the Excel Workbook
strMainSheet = "Main"
If Not rstUnique.EOF Then
'Set the Excel row to start at:
intExcelMainRow = 8
'Set the Excel column to start at:
intExcelMainCol = 3
'get the number of rows in the new recordset
intCaccRows = rstUnique.RecordCount
'this results in an error, not fatal so resume
Set objExcelApp = GetObject(, "Excel.Application")
If objExcelApp Is Nothing Then
Set objExcelApp = CreateObject("Excel.Application")
End If
Set objExcelBook = objExcelApp.Workbooks.Add(strTemplate)
Set objExcelSheet = objExcelBook.Worksheets(strMainSheet)
'let's see the Excel sheet as it's being populated
objExcelApp.Visible = True
'enter the number of rows we are working with
objExcelSheet.Range("B7") = intCaccRows
Do Until rstUnique.EOF
'always write the new sheet value on the main worksheet
strSheet = strMainSheet
Set objExcelSheet = objExcelBook.Worksheets(strSheet)
objExcelSheet.Cells(intExcelMainRow, intExcelMainCol) = rstUnique.Fields("CACC")
'the new worksheet will by called this
strNewSheet = rstUnique.Fields("CACC")
'make a new worksheet for each new CACC
If objExcelBook.Sheets(strNewSheet).Name <> "" Then
'worksheet does not exist, create it
objExcelBook.Sheets.Add(After:=objExcelBook.Sheets(objExcelBook.Sheets.Count)).Name = strNewSheet
End If
'****************************************************
'now add all the detail information for each CACC
'****************************************************
strSheet = strNewSheet
Set objExcelSheet = objExcelBook.Worksheets(strSheet)
'if there is a form filter, we have a where clause
If Len(Me.Filter) = 0 Then
strSQL = "SELECT * FROM qryUnresolvedExcel WHERE CACC = '" & strNewSheet & "'"
Else
strSQL = "SELECT * FROM qryUnresolvedExcel WHERE CACC = '" & strNewSheet & "' AND " & Me.Filter
End If
Set rst = CurrentDb.OpenRecordset(strSQL)
If Not rst.EOF Then
'this is the main data for each datapoint (sheet) item
objExcelSheet.Range("A1") = "Employee: "
objExcelSheet.Range("A2") = "Date: "
objExcelSheet.Range("A1").Font.Bold = 1
objExcelSheet.Range("A1").Font.Underline = True
objExcelSheet.Range("A1").Font.Name = "Calibri"
objExcelSheet.Range("A2").Font.Bold = 1
objExcelSheet.Range("A2").Font.Name = "Calibri"
objExcelSheet.Range("A2").Font.Underline = True
objExcelSheet.Range("B1") = rst.Fields("ServName")
objExcelSheet.Range("B2") = rst.Fields("InspDate")
objExcelSheet.Range("B2").NumberFormat = "mmmm d, yyyy" '"m/d/yyyy"
'Set the Excel row to start at:
intExcelDetailRow = 8
'Set the Excel column to start at:
intExcelDetailCol = 3
'enter the line items for the datapoint
Do Until rst.EOF
objExcelSheet.Cells(intExcelDetailRow, intExcelDetailCol) = rst.Fields("Finding")
objExcelSheet.Cells(intExcelDetailRow, intExcelDetailCol + 2) = rst.Fields("CheckList")
intExcelDetailRow = intExcelDetailRow + 1
rst.MoveNext
Loop
'autofit the cell and center the data
objExcelSheet.Columns("C:C").AutoFit
objExcelSheet.Columns("C:C").HorizontalAlignment = -4108 'xlCenter
rst.Close
Else
rst.Close
Set rst = Nothing
End If
'****************************************************
intExcelMainRow = intExcelMainRow + 1
rstUnique.MoveNext
Loop
Else
intCaccRows = 0
End If
'CLOSE EXCEL REFERENCES:
Set objExcelSheet = Nothing
Set objExcelBook = Nothing
'objExcelApp.Quit
'Set objExcelApp = Nothing
DoCmd.Hourglass False
End Sub
After we are done running our VBA process, we will have an Excel Workbook with multiple sheets:
You can do the same type of Access export to Excel VBA by recreating the above datasheet in a table, and then run the code above.
Let me know if you have questions, and remember that sharing is nice, and may help someone else.
How to Fix Run Time Error 1004 in Excel
If you work with Microsoft Excel frequently, chances ar ling for a solution. Fortunately, this error is well-documented, and there are several ways to resolve it. In this article, we’ll explore the causes of run time error 1004, practical steps to fix it, and preventive measures to reduce the chances of it happening again. What […]
How To Parse A Flat File In Excel VBA
In another post I demonstrated how to access a file on your computer using the MS Office Library. Here it is if you don’t know what I’m talking about. In this post, I am going to show you how to access the file and load it into your spreadsheet. I will do the same thing […]
How to pick a file to load In VBA
How to Pick a File in VBA: FileDialog & GetOpenFilename Explained When building Excel VBA applications, you’ll often need to let users pick a file to load in VBA. Instead of hard-coding file paths, you can use built-in dialogs that make file selection easy and user-friendly. VBA offers two main approaches: FileDialog object (flexible, customizable) […]
How can I interact with other Office applications (Excel) using VBA in Access?
Need to write your Access data or query to an Excel file? Here is the how to do it: Most people are familiar with Excel and know how to use it well (enough), and when you start talking about Access, they get scared off, and don’t know what to do anymore. Well, here you are […]
Support these sponsors: